H'Reers Developer Guide
UI
Table of Contents
- UI
- Setting up, Getting started
- Architecture
- Implementation
- Documentation, Logging, Testing, Configuration, Dev-Ops
- Appendix: Requirements
- Appendix: Instructions for Manual Testing
- Appendix: Planned Enhancements
Acknowledgements
-
This project is based on the AddressBook-Level3 project created by the SE-EDU initiative. (UG, DG, github).
-
We would also like to acknowledge the following external tools and libraries used in our project:
-
Project Lombok – for reducing boilerplate code in our Java classes [Website].
-
Mockito – for facilitating unit testing through mocking [Website].
-
GitHub Copilot – for providing code suggestions during development and quality checks in pull requests [Website].
-
ChatGPT by OpenAI – for providing guidance and suggestions during development and documentation writing [Website].
-
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Architecture
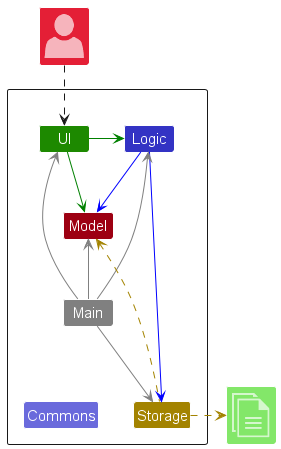
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main (consisting of classes Main and MainApp) is in charge of the app launch and shut down.
- At app launch, it initializes the other components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down, it shuts down the other components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
The bulk of the app's work is done by the following four components:
-
UI: The UI of the App. -
Logic: The command executor. -
Model: Holds the data of the App in memory. -
Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
How the architecture components interact with each other
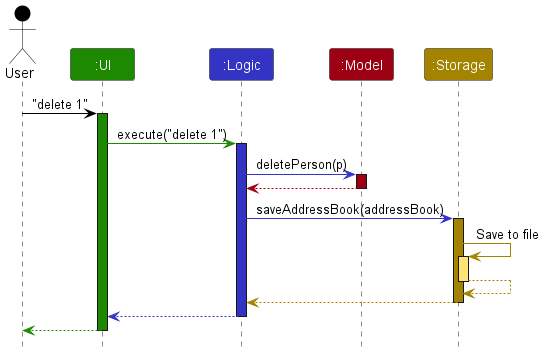
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete 1.
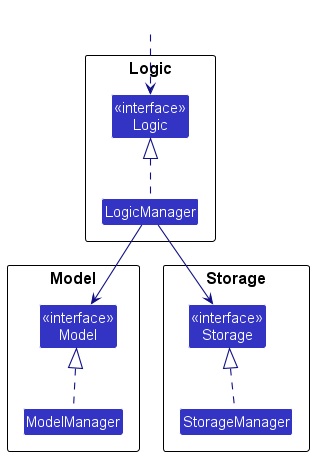
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component's being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
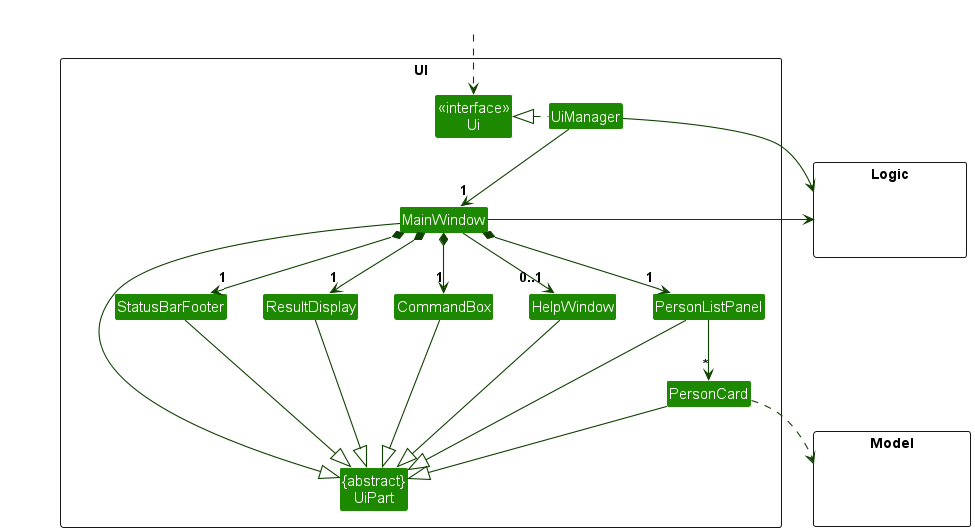
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, PersonListPanel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysPersonobject residing in theModel.
Logic component
API : Logic.java
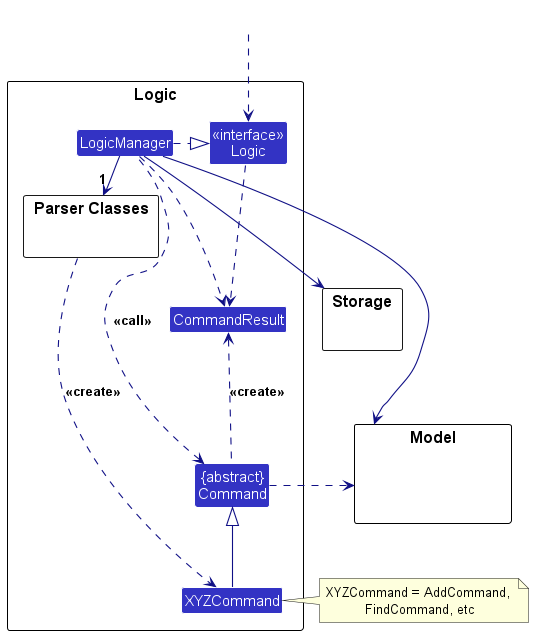
Here's a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component, taking execute("delete 1") API call as an example.
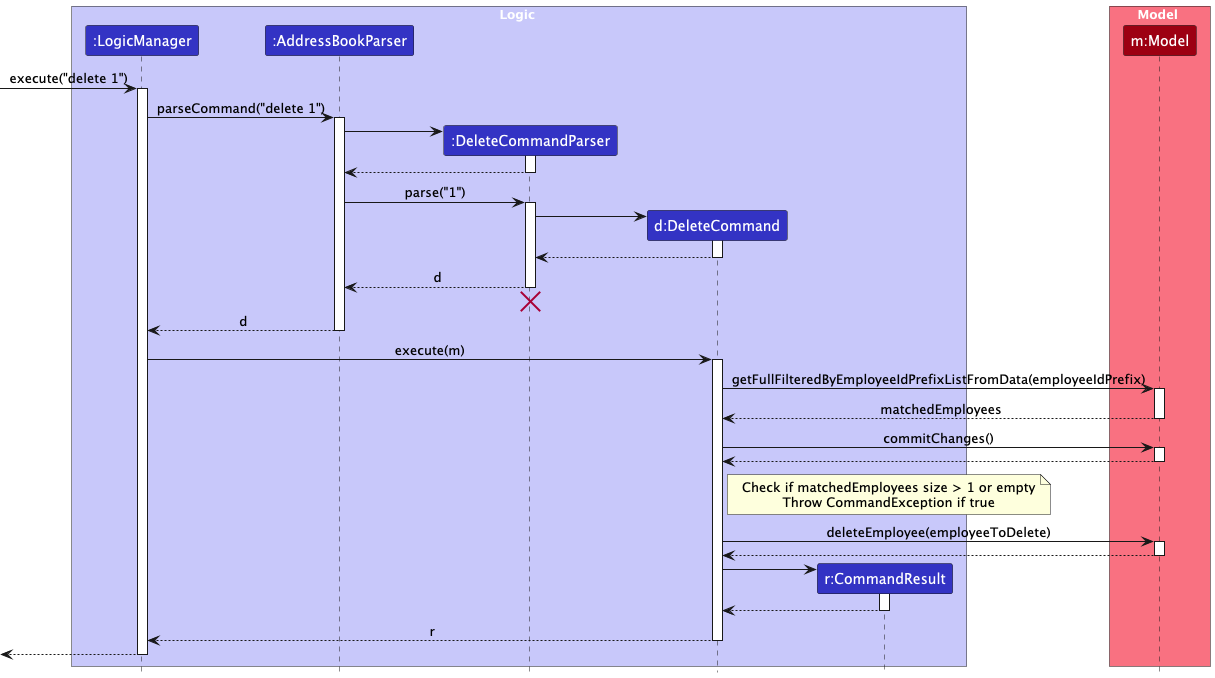
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it is passed to anAddressBookParserobject which in turn creates a parser that matches the command (e.g.,DeleteCommandParser) and uses it to parse the command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,DeleteCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to delete an employee).
Note that although this is shown as a single step in the diagram above (for simplicity), in the code it can take several interactions (between the command object and theModel) to achieve. - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned back fromLogic.
Here are the other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command:
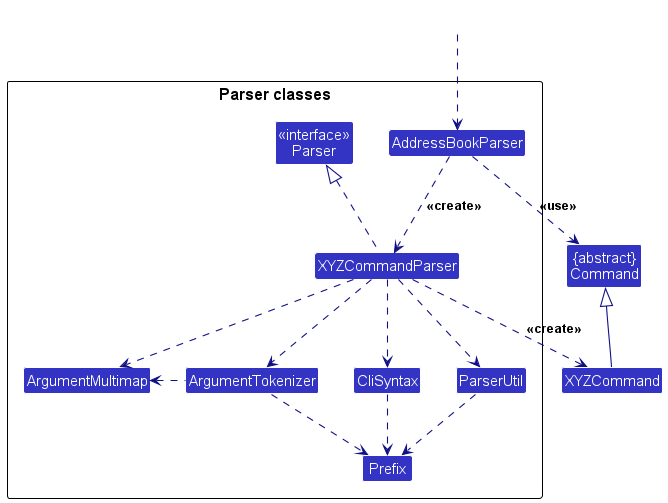
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
AddressBookParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,AddCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandobject (e.g.,AddCommand) which theAddressBookParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddCommandParser,DeleteCommandParser, ...) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
Model component
API : Model.java
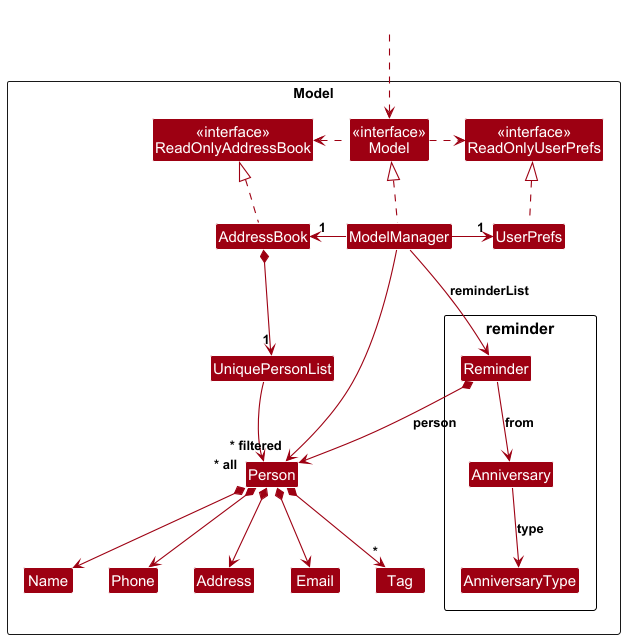
The Model component:
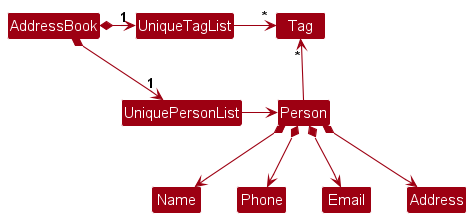
- Stores the address book data i.e. all
Personobjects (which are contained in aUniquePersonListobject). - Stores the currently 'selected'
Personobjects (e.g. results of a search query) as a separatefilteredlist which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Person>that can be 'observed'. For example, the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list changes. - Stores a
UserPrefsobject that represents the user's preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefsobject. - Does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should be able to exist on their own without depending on other components). - Additionally, the model includes data structures for reminders, such as
Reminder,Anniversary, andAnniversaryType. These are used to support the reminder functionality described later in the Implementation section.
Storage component
API : Storage.java
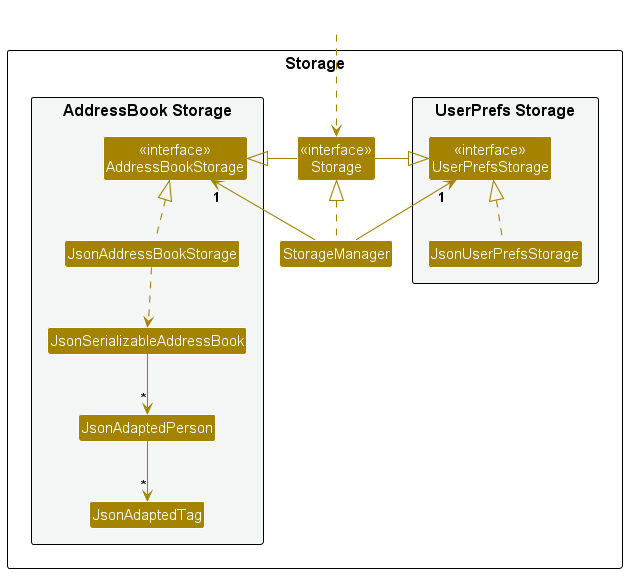
The Storage component,
- can save both address book data and user preference data in JSON format, and read them back into corresponding objects.
- inherits from both
AddressBookStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent's job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel)
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.address.commons package.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
Employee Identification
Our employeeId utilize a UUID based prefix matching system.
The employeeId is generated using the UUID class in Java, which creates a universally unique identifier. This identifier is then used as a prefix for each employee's record, allowing for easy searching and retrieval of information.
Prefix Conflict Restriction
The system strictly enforces that no prefix conflicts can exist between any two employee IDs. A prefix conflict occurs when one employee ID is a prefix of another employee ID (as defined in the glossary). This restriction is necessary for the prefix matching system to work correctly and to ensure unambiguous identification of employees when only a prefix of their ID is provided in commands.
For example, if one employee has the ID abc123 and another employee has the ID abc123456, this would create a prefix conflict because abc123 is a prefix of abc123456, making it impossible to uniquely identify the employee when only the prefix abc123 is provided.
Prefix Matching Logic
The prefix matching logic is primarily managed within the EmployeeId class, which provides methods to check for these conflicts:
-
isPrefixOf(EmployeeId other): Checks if the current ID is a prefix of another ID -
hasPrefixConflict(EmployeeId other): Checks if there's a conflict between two IDs in either direction
The prefix matching logic is primarily managed within the EmployeeId class. The prefix matching logic is mostly used by the Model and AddressBook class, which serves as the facade that maintains the internal UniquePersonsList. This feature is also present in the LogicManager class, where before every command is launched, it triggers a scan throughout the database to check if there are any entries that violate the prefix matching rule, following the lazy validation principle.
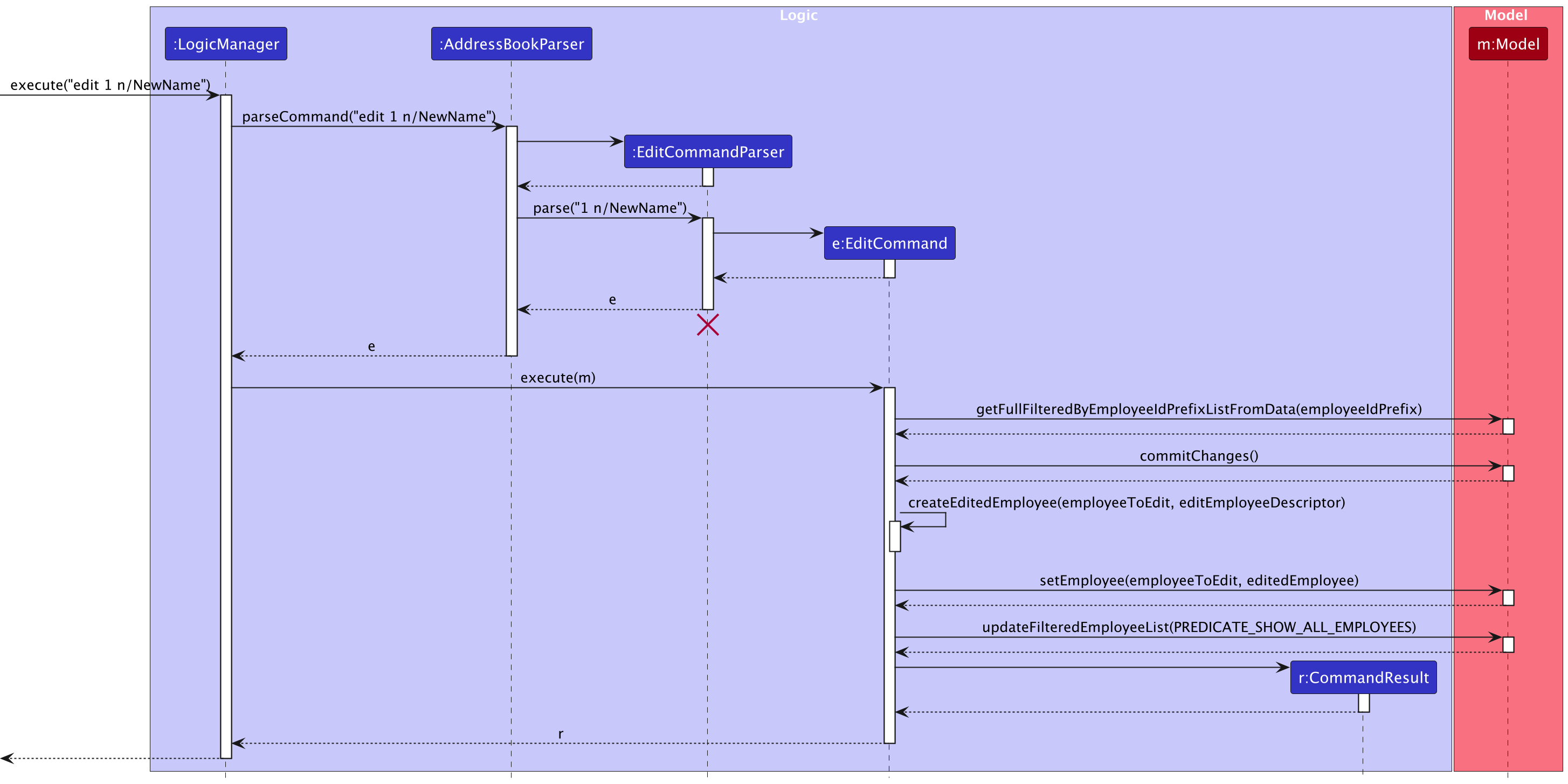
Edit Employee Records
Implementation:
The edit command is implemented by the EditCommand class, which extends the abstract Command class. It works through the following process:
- The
EditCommandParserparses the command input to create anEditEmployeeDescriptorcontaining the fields to be updated. - The command identifies the target employee using the employee ID prefix.
- The system verifies that exactly one employee matches the provided prefix.
- A new employee object is created with updated fields from the descriptor, preserving unchanged fields from the original employee.
- The system validates that the new employee ID (if changed) doesn't conflict with existing IDs.
- The original employee record is replaced with the edited version in the model.
The edit command also supports the undo/redo feature by preserving the previous state via the model's commit function.
AddAnniversaryCommand
Implementation:
The add anniversary command is implemented by the AddAnniversaryCommand class, which extends the abstract Command class. It works through the following process:
- The AddAnniversaryCommandParser parses the command input to extract the employee ID prefix and the anniversary details.
- The command identifies the target employee using the employee ID prefix.
- The system verifies that exactly one employee matches the provided prefix.
- The command checks for duplicate anniversary entries in the target employee's record.
- If no duplicate exists, a new employee object is created with an updated anniversary list, while preserving unchanged fields from the original employee.
- The original employee record is replaced with the updated version in the model.
- A success message is returned confirming the addition of the anniversary.
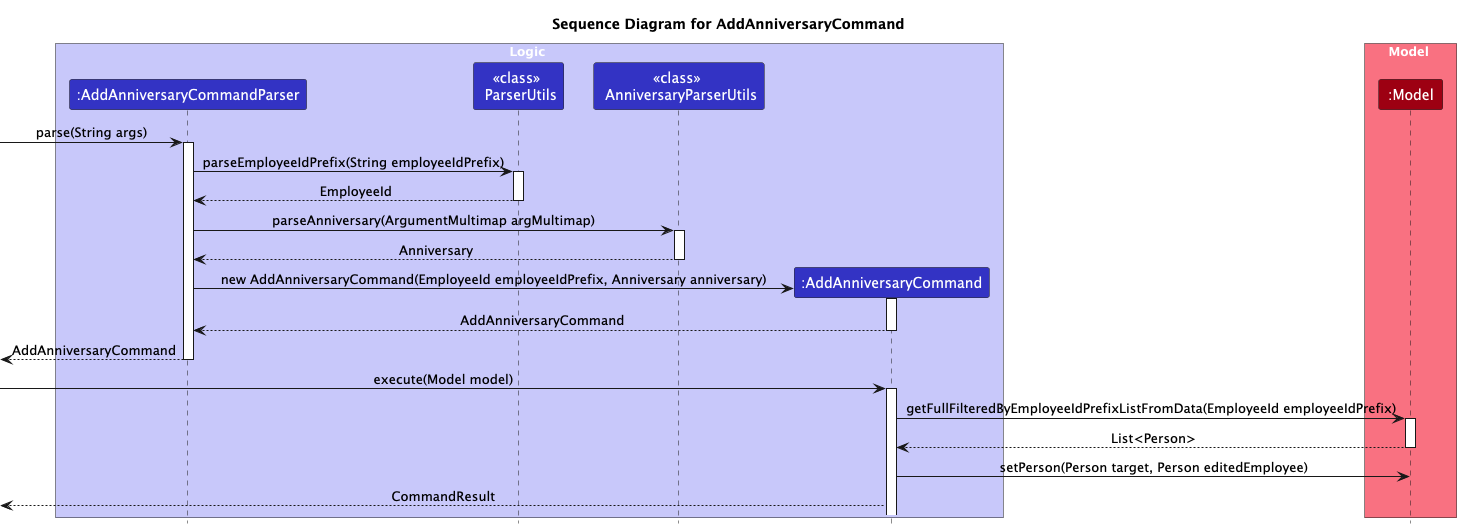
DeleteAnniversaryCommand
Implementation:
- Parsing the Input:
- The DeleteAnniversaryCommandParser tokenizes the input using the PREFIX_EMPLOYEEID (eid/) and PREFIX_ANNIVERSARY_INDEX (ai/). It validates that both required prefixes are present. Missing prefixes trigger a ParseException with the usage message.
- Validating and Converting Input:
- The parser uses ParserUtil.parseEmployeeIdPrefix() to validate and convert the employee ID prefix. It uses ParserUtil.parseIndex() to convert the anniversary index string into an Index object. An additional check confirms that the index is within acceptable bounds (non-negative).
- Identifying the Target Employee:
- In the execute method of DeleteAnniversaryCommand, the system retrieves all employees whose IDs start with the given prefix.
- It verifies that exactly one employee matches:
- If multiple employees are found, it throws a CommandException with a corresponding error message. If no employee is found, it also throws a CommandException.
- Deleting the Anniversary:
- The command retrieves the target employee’s anniversary list. It checks whether the provided index is within the bounds of this list. If valid, the anniversary at the specified index is removed.
- Updating the Employee Record:
- A new employee object is created using the builder pattern with the updated anniversary list while preserving unchanged fields (e.g., employee ID, name, job position, email, phone, tags). The model is updated by replacing the old employee record with the new one.
- Returning the Outcome:
- On successful deletion, the command returns a success message that includes the details of the deleted anniversary.

Reminder Feature
The reminder feature is facilitated by the ReminderCommand. It helps users view upcoming birthdays and other anniversaries by scanning through all stored employees and collecting relevant date-based reminders.
Internally, this feature is supported by:
- The
Remindermodel class – Represents an upcoming event (e.g., birthday, work anniversary) associated with anEmployee. -
Model#updateReminderList()– Gathers all relevant upcoming anniversaries and stores them in an observable list. -
Model#getReminderList()– Provides read-only access to the current list of reminders. -
ReminderListPanelandReminderCardin the UI – Display reminders to the user in the interface.
The ReminderCommand executes the following:
- Calls
Model#updateReminderList()to find anniversaries within the next 3 days. - Each
Reminderis created with anEmployee,AnniversaryType, date, and description. - Results are sorted by upcoming date and stored in an observable list.
- The UI automatically updates by binding to this observable list.
Given below is an example use case showing how the reminder feature behaves step-by-step.
Step 1. The user launches the application, which contains several employee entries with birthday and anniversary dates.
Step 2. The user executes the command:
reminder
This triggers the ReminderCommand, which performs the following steps internally:
- Retrieves all employees via
Model#getFilteredPersonList(). - For each employee, iterates through all anniversaries.
- Checks whether each anniversary is within 3 days from today.
- Creates a
Reminderobject for each upcoming event. - Sorts the list of reminders by date.
- Stores the sorted reminders in an observable list using
Model#updateReminderList().
Step 3. The ReminderListPanel in the UI detects the update in the observable list and renders each reminder using a ReminderCard. Each card shows:
- The employee’s name and job position.
- The type of anniversary (e.g., "Birthday", "Work Anniversary").
- A short description and how soon the event is (e.g., “upcoming in 2 days”).
💡 Note:
- If multiple reminders exist for a single employee (e.g., birthday and work anniversary in the same week), they will each be listed as separate reminders.
- Only anniversaries falling within the next
3days will be displayed. This range is controlled by the constantREMINDED_DATE_RANGE.- All anniversaries, including custom anniversaries, are treated as annual event. Even if user input date is past date (e.g. 2023-04-07), the implementation ignores the year and considers month and date only, producing (2025-04-07).
Sequence Diagram
The following sequence diagram illustrates the steps described above:
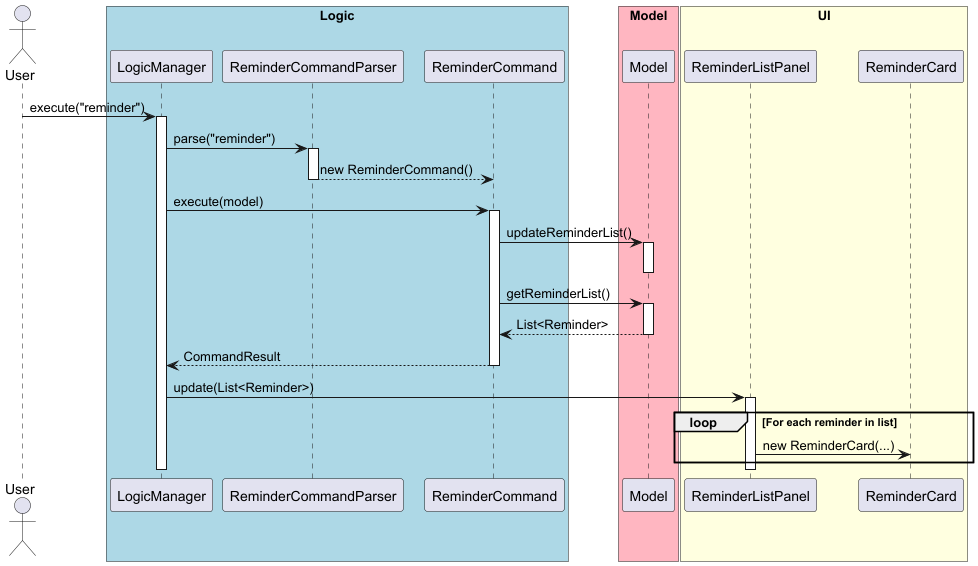
Note: The filtering logic (within 3 days) is abstracted into the model for separation of concerns.
Activity Diagram
The diagram below illustrates the internal logic of how the model filters the reminder list:

The filtering is based on whether an anniversary falls within the next 3 days. In code, this value is stored as a constant:
public static final int REMINDED_DATE_RANGE = 3;
Find Employees Feature
The Find feature allows users to filter and view employees in the address book based on search criteria such as name and job position. This section explains how the feature is implemented and how it behaves under different inputs.
The Find feature is primarily driven by:
-
FindCommand: Executes the filtered search based on a predicate
-
FindCommandParser: Parses user input and builds the corresponding predicate
-
PersonSearchPredicateBuilder: Constructs combined Predicate
from argument values -
Model: Provides access to the filtered employee list and the update mechanism
Given below is an explanation of how the Find feature works:
When a user enters a command such as:
find n/Alice jp/engineer the following steps occur:
Step 1. FindCommandParser uses ArgumentTokenizer to extract the values for prefixes (n/, jp/).
Step 2. It checks for errors such as:
- No valid prefixes
- Empty input values for all fields
- Invalid preamble
If the tokens are valid, it delegates predicate construction to PersonSearchPredicateBuilder.
Step 3. The builder constructs Predicate
- NameContainsKeywordsPredicate
- JobPositionContainsKeywordsPredicate
The two predicates behave slightly differently to suit their field contexts:
- NameContainsKeywordsPredicate uses partial matching.
This allows users to match names using any substring of a word.
-
n/Alimatches with "Alice Tan", "Khalid Ali"
-
- JobPositionContainsKeywordsPredicate uses full-word matching.
A keyword must match a whole word in the job position exactly (case-insensitive).
-
jp/engineermatches "Software Engineer", "Senior Engineer". -
jp/engdoes not match "Software Engineer", "Senior Engineer".
-
This design was decided because:
- Partial matching in names is user-friendly — users often search by fragments of names.
- Full word matching in job titles avoids false positives and returns more accurate results in professional roles.
It combines both search predicates with logical AND so all conditions must be satisfied for an employee to be included in the search results. For example:
find n/Alice jp/engineermatches employees with "Alice" in their name AND "engineer" in their job position.
Meanwhile, each predicate performs keyword-based partial matching (OR logic within the field). For example:
find n/Alice Bobmatches anyone with "Alice" OR "Bob" in their name.
This design was chosen to support both broad and targeted search strategies:
- A user looking for a specific employee is likely to include more fields (e.g., both name and job position).
- A user performing a general search may only filter by a single field, like a partial name.
This flexible approach aims to enable the command to be both intuitive and powerful, depending on the user’s intent.
Step 4: FindCommand executes by calling:
model.updateFilteredEmployeeList(predicate);
The FilteredList<Employee> inside the model is updated, triggering the GUI to reflect the new list.
The diagram below illustrates the sequence of interactions when a user issues the command find n/Alice jp/engineer:

Import Feature
The import feature allows users to load external data from JSON or CSV files into the H'reers address book.
It supports two write modes: append (to merge with existing records) and overwrite (to replace them entirely).
This feature enhances user productivity by allowing them to integrate employee data from external sources such as HR software exports or spreadsheets.
Implementation
The import functionality is primarily handled by the following classes:
-
ImportCommand: Executes the import logic by calling the format converter and updating the model accordingly. -
ImportCommandParser: Parses the user's import command input and constructs anImportCommandwith the appropriate parameters. -
AddressBookFormatConverter: Handles reading from external JSON or CSV files and converting the content into the internalAddressBookdata structure.
Below is a walkthrough of how the feature works at runtime.
Step 1: User executes import command
When the user types a command such as:
import ft/json fp/data/ fn/contacts wm/append
the LogicManager delegates the parsing to ImportCommandParser, which constructs an ImportCommand using the provided arguments.
Implementation
The import functionality is primarily handled by the following classes:
-
ImportCommand: Executes the import logic by calling the format converter and updating the model accordingly. -
ImportCommandParser: Parses the user's import command input and constructs anImportCommandwith the appropriate parameters. -
AddressBookFormatConverter: Handles reading from external JSON or CSV files and converting the content into the internalAddressBookdata structure.
Below is a walkthrough of how the feature works at runtime.
Step 1: User executes import command
When the user types a command such as:
import ft/json fp/data/ fn/contacts wm/append
the LogicManager delegates the parsing to ImportCommandParser, which constructs an ImportCommand using the provided arguments.
Step 2: Input file is read and parsed
ImportCommand calls AddressBookFormatConverter.convert(...), which reads the file based on the given ft (file type), and converts it into an internal AddressBook object.
- If
ft/json, it is parsed using Jackson JSON utilities. - If
ft/csv, it is manually parsed line-by-line and converted into employees.
Step 3: Import is merged or replaces current state
Depending on the wm/ write mode:
-
append: New data is merged with existingAddressBook. Duplicate employees (based on ID) are replaced. -
overwrite: The entire current address book is replaced with the newly imported address book.
Step 4: Model and storage are updated
- After merging or replacing, the model is updated using
model.setAddressBook(), and the new data is committed to storage.
Sequence Diagram
The following sequence diagram illustrates the steps described above:

Export Feature
Implementation:
- Parsing the Input:
- The ExportCommandParser tokenizes the user input using the prefixes for file type (ft/), file path (fp/), and filename (fn/).
- It calls verifyFileTypePresentAndValid from the FilePathResolverUtils to ensure the file type is provided and valid.
- The parser retrieves the optional file path and filename values.
- The final file path is determined by calling FilePathResolverUtils.resolveFilePath(filePath, filename, fileType).
- Command Construction:
- After resolving the file type and file path, a new ExportCommand instance is created with these parameters.
- The command object stores the file type as a string and the file path as a Path object.
- Executing the Export:
- In the execute method of ExportCommand, the command:
- Retrieves the current list of filtered employees from the model.
- Checks whether there are any employees to export; if none, it throws a CommandException.
- Depending on the file type:
- If "json", it calls AddressBookFormatConverter.exportToJson(displayedEmployees, path).
- If "csv", it calls AddressBookFormatConverter.exportToCsv(displayedEmployees, path).
- The export process is logged using the application's logger for tracking purposes.
- Any errors during file writing or conversion result in a caught exception and an appropriate error message.
- Returning the Outcome:
- Upon successful export, the command returns a CommandResult containing a success message with details of the export (number of employees, file type, and resolved file path).

Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile: HR workers in small companies who are responsible for managing employee engagement and morale. These users often have multiple administrative tasks and struggle to keep up with birthdays, anniversaries, and festive greetings. They can type quickly and prefer CLI over GUI.
Value proposition: We can now have assurance that we aren’t missing any customary birthday/festive remarks. ‘H’Reers automates the process of sending custom birthday and anniversary messages for small company HR workers. Optimized for CLI users, it streamlines contact management and ensures timely, personalized greetings, enhancing employee engagement with minimal effort.
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * |
new HR worker using this for the first time | add employees' contact details | easily manage my company's records |
* * * |
HR worker | delete an old employee's records | remove outdated or incorrect information from the system |
* * * |
HR worker | view reminders for upcoming events | be prepared and not miss any anniversary events. |
* * * |
HR worker | view employee's details | know if a certain employee has any anniversarys coming up soon |
* * |
HR worker | go back to the previous page | |
* |
HR worker | have buttons | rest my fingers from typing |
Use cases
Use case 1: Adding an Employee
System: H'Reers
Use case: UC01 - Add New Employee
Actor: HR Worker
Preconditions:
- The system is running.
- The HR worker has valid employee data to input.
Guarantees:
- The employee record is stored successfully in the system.
- If an error occurred, the system remains unchanged.
Main Success Scenario (MSS):
- HR worker chooses to add new employee.
- HR worker enters required details
- If valid, the system adds the employee record to the database.
- The system displays confirmation:
Employee John Doe added successfully.
Alternative Flows:
- If the format is incorrect, an error message is displayed (e.g.,
Error: Invalid date format). - If the email already exists, the system rejects the entry:
Error: Employee already exists.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
-
3a. The given index is invalid.
-
3a1. H'Reers shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case 2: Showing Anniversaries
System: H'Reers
Use case: UC02 - Add New Employee
Actor: HR Worker
Preconditions:
- The employee exists in the system, identified by their Employee ID.
Guarantees:
- The anniversaries associated with the specified employee are displayed.
Main Success Scenario (MSS):
- HR Worker enters the
showAnnicommand with the specified employee’s ID. - H'Reers retrieves the list of anniversaries associated with the employee.
- H'Reers opens a new window or panel displaying:
- Each anniversary’s name, date, and description (if any).
- A confirmation message is displayed, indicating successful retrieval.
- Use case ends.
Extensions:
-
1a. Employee Not Found:
- H'Reers displays an error message indicating that no employee matches the specified ID.
- Use case ends.
-
1b. Preamble Found:
- H'Reers displays an error message indicating that the correct usage of the command.
- Use case ends.
-
3a. No anniversaries found:
- H'Reers displays a new window with no anniversaries found.
- Use case resumes at step 5.
Use case 3: Find Employees
System: H'Reers
Use case: UC03 – Find Employees
Actor: HR Worker
Preconditions:
- The system has at least one employee record stored.
Guarantees:
- Employees matching the specified search criteria are displayed.
- The filtered list replaces the currently displayed list.
- If no employees match the criteria, an empty list is shown.
- The system state remains unchanged.
Main Success Scenario (MSS):
- HR Worker enters the
findcommand with one or more search criteria using supported prefixes (n/,jp/). - H'Reers filters the employee list using a combined predicate and displays the filtered list.
- A success message is shown indicating how many results were found.
- Use case ends.
Extensions:
-
1a. No Prefix Provided:
- H'Reers displays an error message indicating to add at least one prefix.
- Use case ends.
-
1b. Preamble Found:
- H'Reers displays an error message indicating the command format is invalid.
- Use case ends.
-
1c. All Fields Empty:
- H'Reers displays an error message indicating to add at least one prefix.
- Use case ends.
-
2a. No Matching Employees Found:
- H'Reers displays an empty list.
- Use case resume at step 3.
Non-Functional Requirements
- Performance
- Application must start within 3 seconds on standard hardware
- All commands must execute with response time under 1 second
- System must handle up to 1000 employee records without performance degradation
- Reminder calculations must complete within 2 seconds even with maximum load
- Reliability
- Data persistence with automatic saving after any modification
- Backup creation before high-risk operations
- Undo functionality must restore system to previous state with 100% accuracy
- Usability
- The product should be for a single user
- CLI commands must follow consistent syntax patterns
- New HR users should master core functions within 10 minutes
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse
- Error messages must clearly explain issues and suggest corrections
- Compatibility
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
17or above installed. - Data files must maintain backward compatibility with previous versions
- Export formats (JSON, CSV) must be compatible with standard HR tools like Excel
- Maintainability
- Code documentation for all major components
- Minimum 80% unit test coverage
- Modular architecture allowing feature extensions
- Clear separation of concerns between UI, Logic, Model, and Storage components
Glossary
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, MacOS
- Private contact detail: A contact detail that is not meant to be shared with others
- Prefix conflict: When two Employee IDs are such that one ID is a beginning of the other.
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Launch and shutdown
-
Initial launch
-
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
-
Open your command prompt (on Windows) or terminal (on Mac/Linux).
-
Navigate to the folder where you saved the .jar file. For example:
cd /path/to/your/folder -
Run this command:
java -jar hreers.jar- Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimal.
-
-
Saving window preferences
-
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
-
Re-launch the app by running
java -jar hreers.jar.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
-
Core Features
Add Employee Records
Prerequisites:
H'Reers is running.
Test Case 1: Add an employee with birthday and work anniversary
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com
jp/President bd/2001-01-01 wa/2020-07-08
Expected Result:
-
John Doeis added to H'Reers. - His birthday and work anniversary are automatically created.
- Success message is shown confirming the addition.
Test Case 2: Invalid date format
add n/Linda Lee p/98765432 e/lindalee@example.com
jp/Nurse bd/12-01-2000
Expected Result:
- Command fails with error message:
Anniversary date must be in YYYY-MM-DD format. - No employee is added.
Delete Employee Records
Purpose:
Allows HR workers to remove outdated or incorrect employee records.
Command Format:
delete Employee_ID_prefix
Example Commands:
delete abcd12
Outputs:
-
Success:
Deleted Employee: John Doe; Phone: 98765432; Email: johnd@example.com; Job: President; Tags: -
Failure:
Error: Employee not found.
Duplicate Handling:
If multiple employees match, prompt for additional details to ensure correctness.
Edit Employee Records
Purpose:
Allows HR workers to modify existing employee information, such as name, phone number, email, job position, or tags.
Command Format:
edit EMPLOYEE_ID_PREFIX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [j/JOBPOSITION] [t/TAG]... [eid/EMPLOYEE_ID]
Example Commands:
edit abcd12 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.com eid/efgh3123
edit 5678ef n/Jane Smith j/Senior Manager t/management
Parameter Rules:
- EMPLOYEE_ID_PREFIX: Must match exactly one employee in the system
- NAME: Alphabets and spaces only, case-insensitive
- PHONE: Numbers only
- EMAIL: Must contain '@' and valid domain
- JOBPOSITION: Must be a valid job position
- TAG: Alphanumeric words
- EMPLOYEE_ID: Valid UUID format
Outputs:
-
Success:
Edited Employee: [name] Phone: [phone] Email: [email] Job Position: [jobPosition] Tags: [tags] -
Failure: Various error messages depending on the issue:
At least one field to edit must be provided.Multiple employees found with prefix XYZNo employee found with prefix XYZThe new employee ID conflicts with existing employee IDs
Find Employee Records
Prerequisites:
H'Reers is running and has employees:
- Alex Yeoh (Hiring General)
- David Li (Coding Manager)
Test Case 1: Find by name only (partial match)
find n/Alex Li
Expected Result:
- Employee list is filtered to show:
- Alex Yeoh
- Charlotte Oliveiro
- David Li
- Success message is shown: 3 employees listed!
Test Case 2: No prefix provided
find Alice
Expected Result:
- Command fails with:
Invalid command format! - No filtering occurs.
Undo Changes
Purpose:
Allows HR workers to revert the most recent change made to the employee records, such as undoing an added or deleted employee.
Command Format:
undo
Functionality:
- Undo Last Action: Reverts the most recent change made to the employee data. If the last operation was adding a new employee, the employee will be removed. If the last operation was deleting an employee, the employee will be restored.
Outputs:
- Success: Undo successful. Last action reverted.
- Failure: Error: No changes to undo. (This will occur if there are no actions to undo or the history stack is empty.)
Anniversary commands
Purpose:
Allows HR workers to manage employee anniversaries.
Anniversary commands
This section details the manual testings that can be done to commands related to managing employee anniversaries, including adding, deleting, and viewing anniversaries.
Add Anniversary Command
Prerequisites: Ensure the application is running with an existing employee in the database. This employee's employeeID prefix will be termed EID for this section
Test Case 1: Standard Anniversary Creation (Success)
addAnni eid/<EID> d/2024-06-15 an/Company Foundation Day at/Corporate
atdesc/Annual company celebration ad/Celebrating our company's founding
Expected Result: Standard Anniversary Created for the Employee
A new anniversary is added to the employee with ID starting with EID.
The anniversary has
- name "Company Foundation Day"
- date "2024-06-15"
- type "Corporate"
- type description "Annual company celebration"
- description "Celebrating our company's founding".
Success message: "New anniversary added: [anniversary details]" is displayed.
Test Case 2: Missing EmployeeId (Failure)
addAnni d/2024-06-15 an/Company Foundation Day at/Corporate
Expected Result: Standard Anniversary Creation Failed
No anniversary is added. Error message: "Invalid command format! [usage information]" is displayed.
Test Case 3: Malformed Date (Failure)
addAnni eid/EID d/15-06-2024 an/Company Foundation Day at/Corporate
Expected Result: Standard Anniversary Creation Failed
No anniversary is added. Error message: "Anniversary date must be in YYYY-MM-DD format." is displayed.
DeleteAnniversaryCommand
Prerequisites: Ensure the application is running with an existing employee in the database, with at least one anniversary associated, except for test case 2. This employee's employeeID prefix will be termed EID for this section.
Test Case 1:Standard Anniversary Deletion (Success)
deleteAnni eid/EID ai/1
Expected Result: Standard Anniversary Deletion Successfully executed
Anniversary with index 1 is removed from the given employee Success message: "Anniversary deleted: [anniversary details]" is displayed.
Test Case 2: Employee has No anniversary (Failure)
Prerequisite : Ensure the application is running with an existing employee with no anniversary.
deleteAnni eid/EID ai/1
Expected Result: Standard Anniversary Deletion Failed
No anniversary is deleted. Error message: "The index you are searching for is out of bounds for the anniversary." is displayed.
Test Case 3: Missing EmployeeId (Failure)
Test case: deleteAnni eid/ ai/1
Expected Result: Standard Anniversary Deletion Failed
No anniversary is deleted. Error message: "Invalid command format! deleteAnni: deletes an anniversary to the employee identified by a prefix of their Employee ID. Parameters: eid/EMPLOYEE_ID ai/index " is displayed.
Show Anniversary Command
Prerequisites:
H'Reers is running and has employee:
- Alex Yeoh (eid: 4b190...)
Test Case 1: Show anniversaries for an employee with no anniversaries
Edit the eid accordingly.
showAnni eid/4b190
Expected Result:
- A new window opens.
- The anniversary list is empty.
- Success message is still shown: Anniversaries shown for employeeId [full Eid]
Test Case 2: Invalid command format (missing prefix)
showAnni 4b190
Expected Result:
- Command fails with: Invalid command format!
- No window opens.
showAnni eid/EMPLOYEE_ID
Example Commands:
showAnni eid/efgh3123
File Management
Export Command
Prerequisites: Ensure the application is displaying some data of choice, except for test case 5
Test Case 1:Standard JSON Export (Success)
export ft/json
Expected Result:
a json file containing data that is currently being displayed beside the jar file in an /output/ directory.
Success message: "Exported
Test Case 2:Standard CSV Export (Success)
export ft/csv
Expected Result:
a csv file containing data that is currently being displayed beside the jar file in an /output/ directory.
note that the csv file will contain multiple rows of the same employee should the employee had multiple anniversaries
Success message: "Exported
Test Case 3:Standard JSON Export With Name (Success)
export ft/json fn/contacts
Expected Result:
a json file containing data that is currently being displayed beside the jar file as contacts.json
Success message: "Exported
Test Case 4:Standard JSON Export With Name and File Path (Success)
export ft/json fn/contacts fp/./output/kraken
Expected Result:
a json file containing data that is currently being displayed beside the jar file as
Test Case 5:Export With Nothing Shown (Failure)
find n/<some name that does not exist in the database>
export ft/json
Expected Result:
Error message: "No people to export." is displayed.
Import Command
Prerequisites:
- Ensure a valid json file exists for test case 1-2, this can be created via export
- a valid csv file exists for test cases 3-4, this can be created via export command
- tests requiring empty files can be created by creating a new file with correct file extension and no content
- formats that do not conform to the exported files may cause errors.
- csv files that have been opened by microsoft excel can cause error, due to excel's
smart formattingfeatures, which may cause the file to be saved in a different format, and the formats of columns to be changed - ensure that csv files that have been created conform to all the required rules set in the User Guide, such as requiring the file to be saved in utf-8 format.
- Any non-compliance of the rules mentioned above and the rules in the user guide may cause the import to fail, and we do not guarantee their successes. Extreme cases may even cause silent failures.
- Especially for Arabic language settings or Japanese word settings where the input goes from right to left, we do not support such encodings.
- Ensure that for valid cases, the file path is correct, and the file exists in the specified location.
- We will assume that the export section has been done prior, and will use the files created accordingly.
- note that duplicated fields will be allowed for json. For single fields, the bottommost field will be used, and the rest will be ignored. This is due to not using
JSONPARSER_STRICT, to allow some flexibility in the file format. - no embedded newlines into fields are allowed.
Test Case 1:Standard JSON Import Overwrite (Success)
import ft/json fp/./output/ fn/output wm/overwrite
Expected Result ( no issues ):
your current app will be overwritten by file content
Success message: "Successfully imported
Expected Result ( has issues ):
your current app will not be overwritten by file content
- omitted field : "Invalid data in import file: Employee's
field is missing!" is displayed - prefix collision ( an employee prefix in the file collides with another employee prefix in the file ) : "Found multiple employees with employeeId starting with
= " is displayed - identity collision ( same employeeId, different details ) : "conflicting records found
\n " is displayed - invalid file : "Failed to read the file: the json file is invalid or corrupted." is displayed
- empty file : "The JSON file is empty. Please provide a valid file." is displayed
Test Case 2:Standard Json Import Append (Success)
import ft/json fp/./output/ fn/output wm/append
Expected Result:
your current visual appended by file content.
this test case subsumes all of the file related errors that is presented above
note that the append mode will result in the following regressive effects
- if the app currently contains employees with the same EmployeeId , name, email, phone, tags, job position, the anniversaries within the json file will be merged into the existing employees
- if the app currently contains employees with the same EmployeeId, but differ in any of the other fields, the employees will be put into omitted list for manual conflict resolution, that will be displayed.
- if the app currently contains employees that have a EmployeeId that is a Prefix of an employee currently present in the app, the employees will be put into omitted list for manual conflict resolution, that will be displayed.
- If the file contains employees that are not present in the app, they will be added to the app.
Expected Result ( no conflicts ):
Success message: "Successfully imported
- Conflicting records found: " is displayed.
Expected Result ( has conflicts - ):
Success message: "Successfully imported <number - 1> contacts, skipped 1. Please resolve conflicts manually
- Conflicting records found:
" - is displayed.
Test Case 3:Standard CSV Import Overwrite With Name (Success)
import ft/csv fp/./output/ fn/output wm/overwrite
Expected Result:
note that the csv mode will result in the following regressive effects
- all lines with the same employeeId and name, email, phone, tags, job position will be merged into a single Employee.
Expected Result ( no issues ):
your current visual overwritten by file content
Success message: "Successfully imported
Expected Result ( has issues ):
- omitted field : "Invalid data in import file: Employee's
field is missing!" is displayed - prefix collision ( an employee prefix in the file collides with another employee prefix in the file ) : "Found multiple employees with employeeId starting with
= " is displayed - identity collision ( same employeeId, different details ) : "conflicting records found
\n " is displayed - missing column : "CSV missing required field:
" is displayed - extraenous column :
- empty file : "CSV data cannot be empty." is displayed
Test Case 4:Standard CSV Import Append With Name (Success)
import ft/csv fp/./output/ fn/output wm/append
Expected Result:
this test case subsumes all of the file related errors that is presented above
note that the append mode will result in the following regressive effects
- if the app currently contains employees with the same EmployeeId , name, email, phone, tags, job position, the anniversaries within the json file will be merged into the existing employees
- if the app currently contains employees with the same EmployeeId, but differ in any of the other fields, the employees will be put into omitted list for manual conflict resolution, that will be displayed.
- if the app currently contains employees that have a EmployeeId that is a Prefix of an employee currently present in the app, the employees will be put into omitted list for manual conflict resolution, that will be displayed.
- If the file contains employees that are not present in the app, they will be added to the app.
Expected Result ( no conflicts ):
Success message: "Successfully imported
- Conflicting records found: " is displayed.
Expected Result ( has conflicts - ):
Success message: "Successfully imported <number - 1> contacts, skipped 1. Please resolve conflicts manually
- Conflicting records found:
" - is displayed.
Save Employee Records
Purpose:
Ensures employee records persist across sessions.
Command Format:
- Automatically saves every 30 seconds.
Outputs:
-
Success:
Save occurred successfully. -
Failure:
Save failed -> reverting to backup file.
Additional Targets:
- Full flush backup (complete overwrite).
- Intermediate .tmp file for autosave.
Reminder Feature
1. Listing upcoming reminders
-
Prerequisites: The application should contain employees with anniversaries (e.g., birthday, work anniversary) within 3 days from today.
-
Test case:
reminderExpected: A list of reminders is shown in the side panel. Each entry includes the employee’s name, job position, the type of anniversary, and how soon it will occur (e.g., “in 2 days”). -
Test case:
reminder(when there are no upcoming anniversaries) Expected: The side panel is updated to show an empty list.
2. Reminder display formatting
-
Reminder card fields to verify:
- Employee Name: Matches the name in the employee list.
- Employee ID: Matches the ID in the list.
- Job Position: Matches the employee’s job title.
-
Anniversary Type + Description: Shown as
Birthday - John’s birthdayorWork Anniversary - Joined in 2019, depending on type and description. - Date Display: Shows relative time (e.g., “in 1 day”, “in 3 days”).
-
Manual verification:
- Verify that reminders are sorted by date (soonest anniversary appears first).
- Verify that if an employee has multiple upcoming anniversaries, they appear as separate entries.
- Confirm that expired or future anniversaries outside the 3-day window are not shown.
-
Edge case testing
-
Test case: Add a birthday dated exactly 3 days from now → Run
reminder- Expected: Reminder card for this birthday appears in the list.
-
Test case: Add a birthday 4 days from now → Run
reminder- Expected: No reminder card shown.
-
Test case: Add both a birthday and a work anniversary for the same employee within 3 days
- Expected: Two separate reminder cards are shown, one for each anniversary.
-
Test case: Add reminders for multiple employees
- Expected: All applicable reminders appear and are correctly sorted by date.
Appendix: Planned Enhancements
Team Size: 5
In future versions of H'Reers, the following enhancements are planned to improve functionality, user experience, and data consistency:
-
Address the fullscreen bug issue for all new windows
- Current Issue: Closing windows in fullscreen may cause it to crash.
-
Method to recreate
- When running the app
- Open the app in fullscreen
- Type help
- Close help window
- Repeat 3 and 4 enough times and the app will crash
- Current Workaround: Do not use fullscreen mode.
- Planned Solution: Investigate the cause of the crash and implement a fix to ensure that closing windows in fullscreen mode does not lead to application crashes. It is probably a bug in the JavaFX library.
-
Address the fullscreen bug issue for all new windows
- Current Issue: Closing anniversary window when the screen is tiled with the anniversary window and the main window, will cause it to crash
-
Method to recreate
- Open app
- Type showAnni xxx
- Fullscreen app and tile them side to side
- Close anni window
- App stops running and hangs
- Current Workaround: Do not use fullscreen mode.
- Planned Solution: Investigate the cause of the crash and implement a fix to ensure that closing windows in fullscreen mode does not lead to application crashes. It is probably a bug in the JavaFX library.
-
Stop enforcing the absence of prefix conflicts
- Current Issue: Enforcing prefix conflicts policy may lead to the situation when no employee addition is possible, as every id would conflict with the existing ones. That would occur when the ids of the employees are very short and fill up all the possible beginnings of the ids.
- Current Workaround: The possibility of such a situation is very low, as the ids are generated randomly and are long enough. The only situation when this may occur is when user deliberately made the ids short. This restriction is documented in the user guide.
- Planned Solution: We plan to stop requiring the absence of prefix conflicts. Instead, to disambiguate the employee id reference, we require the user to put $ after the full employee id as a terminator, so that the system will know that the user is referring to the full employee id and not just a prefix.
-
Import Data from Different Formats
- Current Issue: Limited feature functionality to various different csv formats available, and lacks robustness in parsing and validation.
- Current Workaround: mention in the user guide to prevent users from using unsupported formats, to follow the export feature's csv format.
- Planned solution: Use external libraries to support more formats and provide better parsing and validation. This will allow users to import data from various sources without worrying about format compatibility.
-
Observer Support for ShowAnni
- Current Issue: ShowAnni currently does not update dynamically should there be operations on it while the GUI is open.
- Current Workaround: After each operation on Anniversaries, showAnni should be closed and called again.
- Planned solution: We plan to observe GUI means for the UI to automatically update, either by exploring JavaFX GUI observer related options
-
ShowAnni Window is not brought back to screen after it has been minimized
- Current Issue: ShowAnni currently does not reappear when the showAnni command is called after the popup has been minimized. This might be hard for users to see and understand that their call is working and actually showing the anniversaries.
- Current Workaround: Place this under known issues.
- Planned solution: investigate if JavaFx provides methods to specifically avoid this issue (Same as AB3).
-
Enhanced Phone Number Validation
- Current Issue: Phone Numbers cannot have spaces in their format. They also have a limit of 17 digits, which is just to make it not too long
- Planned Solution: Validate phone numbers according to local and international standards, requiring a minimum of 7 digits and ensuring numbers are valid for practical use cases as well as allow spaces between digits.
-
Inconsistency between showAnni and edit/delete syntax
-
Current Issue: For now, edit and delete command has the following syntax:
[edit/delete] [employeeId] [other arguments] - While the syntax of showAnni is:
[showAnni] eid/[employeeId] - which constitutes an inconsistency with the requirement of prefix before employeeId, although it's mandatory to have employeeId with the showAnni command, just as it is with the edit/delete commands.
- Planned Solution: Make the explicit specification of eid/ prefix unnecessary within showAnni, as the command cannot be used without employeeId anyway.
-
Current Issue: For now, edit and delete command has the following syntax:
-
Greater Support for Anniversary recurrence
- Current Issue: For now, only a yearly recurrence is supported.
- Planned Solution: Allow greater options for recurrence, such as monthly, weekly, or custom intervals. This will allow users to set reminders for anniversaries that occur more frequently than once a year.